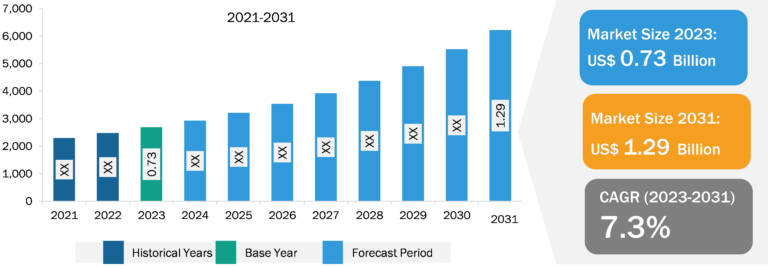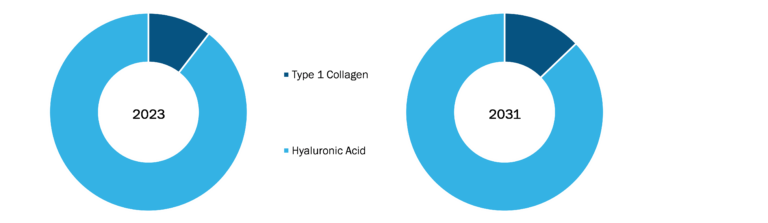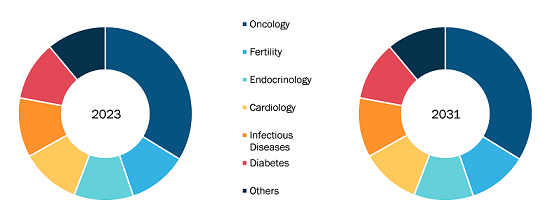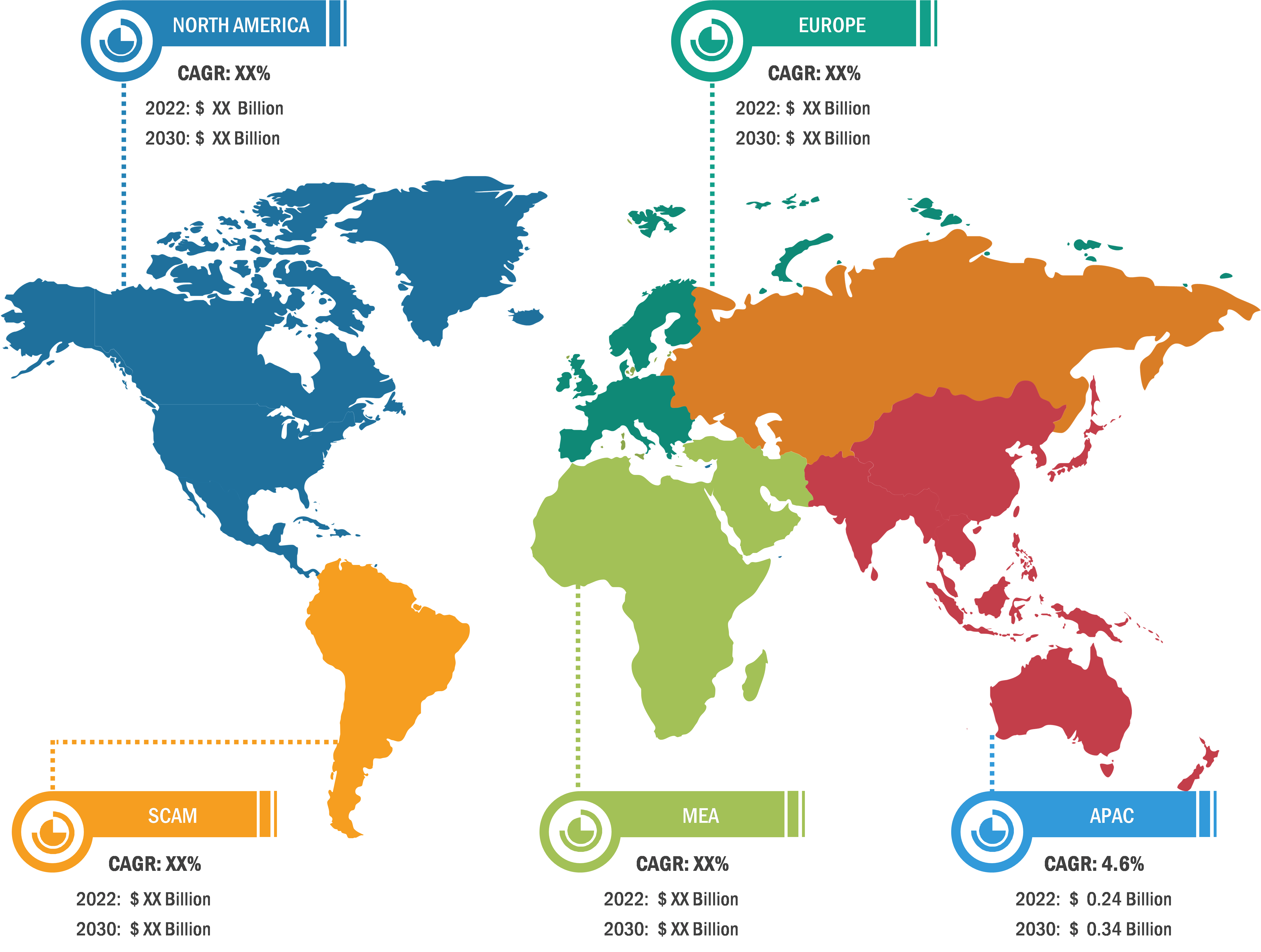
Aquatic Veterinary Treatment Market
In aquaculture practices, there is a high chance of pathogenic outbreaks, which affect farm production. Vaccination is a simple, reliable, and preventative technique of aquatic disease control. Growing aquaculture industry, increasing prevalence of infectious diseases among aquatic animals, and surging demand for aquatic animal species for consumption are the noteworthy factors contributing to the expansion of the aquatic veterinary treatment market size. The market is growing with initiatives taken by various governments to develop their respective aquaculture industries. However, strict regulatory policies for the approval of vaccines hinder the aquatic veterinary treatment market growth.
Increasing Prevalence of Infectious Diseases in Aquatic Animals Drives Aquatic Veterinary Treatment Market Growth
Aquaculture is the world’s fastest-growing food production sector, and similar to other animal-rearing systems, e.g., poultry, cattle, and sheep, disease represents an important obstacle to production that must be dealt with. However, for aquatic animals (including fish, shellfish, shrimp, and others), matters are more complicated, as over 500 such species are farmed commercially, and numerous are affected by specifics that target only them.
Fish are the largest traded food commodity in international trade, with exports worth approximately US$ 150 million. The globalization of aquatic animal products and the growth of aquaculture as a primary supplier of the world’s aquatic food supply have been linked to the cultivation of new aquatic species, the movement of aquatic organisms to new countries and continents, and an overall trend toward the intensification of production procedures and the industrialization of the sector.
While this has opened up new markets for farmed aquatic animals, it has also encouraged the spread of pathogens and diseases. As per the study titled “Prevalence of Anisakid Nematodes in Fish in China,” published by the National Library of Medicine in February 2022, the anisakid nematodes were widespread in fish across China with a pooled incidence rate of 45.5% and the occurrence percentage for fresh fish was the highest, accounting for 58.1%. Eastern China had the maximum prevalence rate of anisakid nematodes (55.3%). According to the data published in the Aquaculture Research & Development journal, ~219 cases of infectious diseases in the fresh aquaculture sector were registered from 2014 to 2018. Among these, 74.88% were parasitic, 12.80% were bacterial, 10.50% cases were a mix of parasitic and bacterial diseases, and 1.83% were viral.
These factors have all contributed to a greater reliance on veterinary medications to ensure successful production by preventing and treating diseases, ensuring healthy stocks, and maximizing output.
Diseases are a major constraint on the culture of many aquatic species; hence, antimicrobial veterinary treatment options are widely used in aquaculture around the world. The indiscriminate use of these veterinary medicines in aquaculture contributes to the spread of antibiotic resistance.
One of the most important strategies for disease prevention in aquaculture and other aquatic animal species is the cautious use of veterinary drugs. It is widely acknowledged that the use of medicines is critical in illness control. According to the World Health Organization, antimicrobial medicines are important for the treatment of bacterial infections in both humans and animals. Therefore, the high prevalence of infectious diseases boosts the demand for appropriate treatment in aquatic animals, which provides lucrative opportunities for the aquatic veterinary treatment market growth in the coming years.
Aquatic Veterinary Treatment Market: Segmental Overview
The aquatic veterinary treatment market is segmented on the basis of treatment, species, disease source, and route of administration. Based on disease source, the market is categorized into bacterial, viral, parasites, and others. The bacterial segment held a significant aquatic veterinary treatment market share in 2022 and is expected to register the highest CAGR during 2022–2030. Bacteria are ubiquitous in aquatic environments, and they play crucial roles in the ecology and health of aquatic animals. Although they can be harmless or beneficial to aquatic animals, some species can cause diseases and infections, affecting the yield and financial performance of the aquaculture sector. Understanding the sources and dynamics of bacteria in aquatic environments is important for maintaining the health and welfare of aquatic animals growing in natural habitats or managed settings such as aquaculture facilities or aquariums. Implementing good management practices, regular monitoring, and appropriate biosecurity measures can help mitigate the risks associated with pathogenic bacteria in aquatic animal systems.
Most bacterial pathogens affecting aquatic animals such as fish are gram-negative and aerobic rod-shaped bacteria (bacilli). Major bacterial diseases affecting salmon are vibriosis (Listonella anguillarum and V. spp.), cold water vibriosis (Vibrio salmonicida), wound disease (Moritella viscosa), flavobacteriosis (Flavobacterium psychrophilum), and bacterial kidney disease (Renibacterium salmoninarum).
Aquatic Veterinary Treatment Market: Competitive Landscape and Key Developments
Merck & Co. Inc., Elanco Animal Health Inc., Zoetis LLC, HIPRA, Phibro Animal Health Corp, Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health, Nisseiken Co. Ltd., VETERQUIMICA S.A., Microsynbiotix, and AquaTactics Fish Health are a few of the key companies operating in the market. These companies focus on product innovation strategies to meet evolving customer demands, along with maintaining their brand name in the aquatic veterinary treatment market.
A few of the recent developments in the global aquatic veterinary treatment market are mentioned below:
- In September 2023, Innocon, a Chilean technology company, developed oral vaccines for salmon farming, with a special focus on preventing Salmonic Rickettsial Septicemia (SRS). SRS is a bacterial disease, representing a considerable challenge for the salmon industry.
- In April 2021, ICAR-CIBA launched CIBA-Nodavac-R, a recombinant vaccine against viral nervous necrosis (VNN), in India’s milestone for aquaculture vaccine development. VNN affects many marines, brackishwater, and freshwater fish and is caused by red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) in fingerlings. CIBA-Nodavac-R is an injectable recombinant VNN vaccine that can effectively prevent VNN.