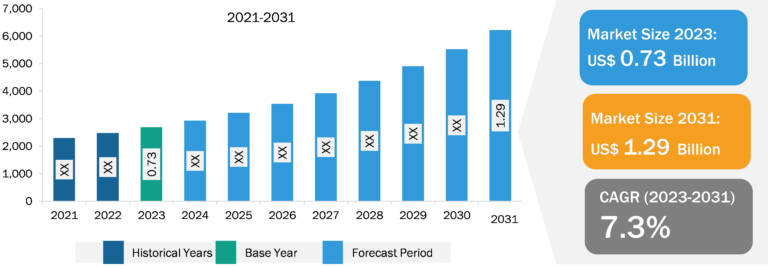
Minimal residue disease testing Market
Minimal residual disease testing is performed to detect and quantify small numbers of cancer cells in a patient’s body. It includes sensitive technologies such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation sequencing (NGS), and flow cytometry to identify residual disease at the molecular level. Minimal residual disease testing is clinically important because it helps monitor response to treatment, predicts risk of relapse, guides personalized therapies, and serves as an endpoint in clinical trials. The increasing global prevalence leukemia, lymphoma, and solid tumors, among others, contributes to the growing demand for minimal residue disease testing products and services.
The minimal residue disease testing market in North America was valued at US$ 0.93 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach US$ 2.34 billion by 2031; it is expected to register a CAGR of 12.12% during 2023–2031. The increasing incidence and prevalence of hematologic cancer in the US are likely to reflect the high risk of survivors having residual cancer cells. According to statistics published by the American Cancer Society, in 2022, there were 34,470 new cases of multiple myeloma and about 6,660 new cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in the US. The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society estimated ~90,390 new diagnoses of lymphoma in the US in 2021, including 8,830 cases of Hodgkin’s lymphoma and 81,560 cases of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. In November 2022, Natera received a national minimal residual disease testing contract from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) National Precision Oncology Program to provide MRD and monitoring services using the company’s Signetera MRD test. In February 2022, the Biomarkers Consortium (BC) of the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) launched a project to validate new methods for quantifying and detecting MRDs. The strong MRD reimbursement framework further facilitates the rollout of new testing products in the region.
Increasing Investments and R&D by Companies to Create Market Opportunities in Coming Years
In April 2023, Foresight Diagnostics closed a Series B financing round led by Foresite Capital and raised US$ 58.75 million to commercialize a highly sensitive liquid biopsy minimal residue disease testing platform. The financing round was headed by Foresite Capital, with the involvement of Bluebird Ventures, Civilization Ventures, Pear Ventures, Stanford University, Agent Capital, and the University of Colorado Healthcare Innovation Fund. Adela, Inc., an innovator in blood testing to monitor minimal residual disease and detect cancer in early stages through a genome-wide methylome approach, announced the closing of the financing of US$ 48 million in September 2023. This financing round included existing investors F-Prime Capital, Deerfield Management, Decheng Capital, OrbiMed, and RA Capital Management, along with Labcorp, a global leader in innovative and comprehensive laboratory services, as a new investor—bringing the company’s total capital to US$ 108 million.
Cancer research centers are also involved in detecting MRD in cancer patients. For example, in September 2023, Myriad Genetics collaborated with Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center to evaluate the use of minimum residual disease testing in breast cancer patients. The research project was planned with the utilization of Myriad’s MRD testing platform, a tumor-informed high-resolution assay based on whole-genome sequencing, for achieving high sensitivity and specificity for circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Thus, the increasing research funding in the area of minimal residue disease testing, as well as the participation of companies in investment initiatives, is expected to boost market growth in the coming years.
Burgeoning Use of Next-Generation Sequencing Technology to Drive Market Growth in Coming Years
NGS offers higher sensitivity than conventionally used morphological and cytogenetic tests. According to the article “A new next-generation sequencing strategy for the simultaneous analysis of mutations and chromosomal rearrangements at the DNA level in patients with acute myeloid leukemia,” published in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics in January 2020, next-generation sequencing has proven to be a promising approach in detecting all genomic lesions in a single run. In addition, NGS applies to any newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia because patients often experience multiple molecular aberrations.
The detection of minimal residual disease has become easier with the introduction of various next-generation error-correcting methods. Molecular barcodes have recently been used to develop several error-corrected next-generation sequencing approaches, which involve barcoding the individual DNA molecules used to create next-generation sequencing libraries. According to the article “Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring with Next-Generation Sequencing,” published in June 2021 by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, next-generation sequencing has been found to have the potential to reduce the prevalence of undiagnosed minimal residual disease. This enables early treatment, which is crucial for the survival of patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL).
In January 2020, Adaptive Biotechnologies collaborated with GlaxoSmithKline to use the clonoSEQ assay to assess minimal residual disease (MRD) in GSK’s hematology product portfolio. Such investments in R&D activities, the introduction of advanced technologies, and increasing focus on developing assays to simplify the assessment of minimal residual disease are likely to boost the growth of the minimal residue disease testing market during the forecast period.
Minimal Residue Disease Testing Market: Technique Overview
Based on technique, the minimal residue disease testing market is divided into flow cytometry, PCR, NGS, and others. The flow cytometry segment held the largest market share in 2023, and the PCR segment is likely to register the highest CAGR of 12.39% during 2023–2031. The largest market share of the flow cytometry segment is due to its high sensitivity and wide applicability for minimal residual disease testing. Evaluating individual cells using flow cytometry determines whether certain protein markers are present on the cell surface. Reliable results need a recent bone marrow sample. Specific antibodies are applied to the bone marrow sample that binds to cells with a specific protein. The sensitivity of this method is evident from its ability to detect a cancer cell from 10,000–100,000 healthy bone marrow cells, subject to the configuration of the flow cytometry. Availability of results may take less than a day.
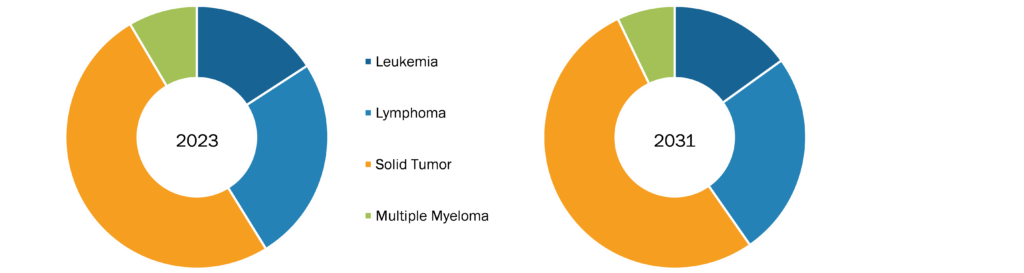
In terms of cancer type, the minimal residue disease testing market is segmented into leukemia, lymphoma, solid tumors, and multiple myeloma. The solid tumors segment held the largest market share in 2023, and the same segment is estimated to grow at the fastest CAGR during 2023–2031. The lymphoma segment held the second largest market share in 2023. The lymphoma segment held the second largest share in the market owing to the increasing prevalence of lymphoma. According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 90,300 people were diagnosed with lymphoma in the US in 2021; the disease burden is expected to increase with each passing year. The most common symptoms of lymphoma include swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin.
Minimal residue disease testing Market: Competitive Landscape and Key Developments
Adaptive Biotechnologies; Natera; Bio-Rad Laboratories; F-Hoffmann La Roche Ltd; Guardant Health; LabCorp; Sysmex Corporation; ARUP Laboratories; Invivoscribe, Inc.; NeoGenomics Laboratories, Inc.; and Mission Bio, Inc are among the key companies operating in the minimal residue disease testing market.
Recent Developments:
Companies operating in the minimal residue disease testing market adopt mergers and acquisitions as key growth strategies. As per company press releases, a few recent market developments are listed below:
- In April 2023, Adaptive Biotechnologies collaborated with Takeda in a translational partnership to deploy its clonoSEQ assay across Takeda’s hematologic malignancy treatment offerings, enabling the detection of minimal residual disease.
- In February 2022, Invitae launched a study to obtain real-world data on personalized minimal residual disease testing across different tumor types.
- In October 2021, Sysmex Inostics, Inc. launched a clinically validated liquid biopsy test based on next-generation sequencing for detecting minimal residual disease associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
- In February 2021, Guardant announced the launch of the Reveal Liquid Biopsy test to monitor residual disease and recurrence in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer. This test improves the treatment of early-stage CRC patients by detecting ctDNA in the blood after surgery to identify patients with residual disease.