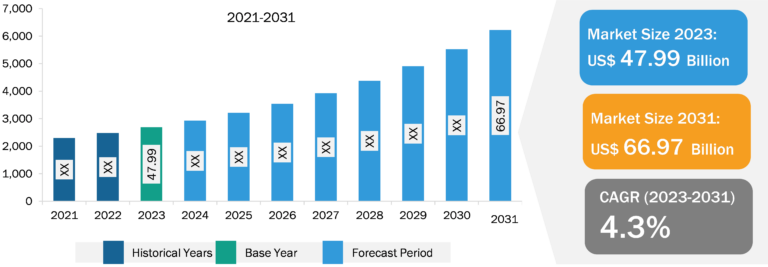
Scandium Market
In 2023, Asia Pacific held a significant share of the scandium market. Rapid economic progress and industrialization in Asia Pacific bolster the demand for high-performance materials to support infrastructure development and urbanization. Asia Pacific is home to some of the world’s largest and fastest-growing aerospace and automotive industries, which are major consumers of lightweight and high-strength scandium-containing alloys. These alloys are particularly valuable in aircraft components, automotive parts, and structural materials, among other applications, wherein reducing weight while maintaining performance is crucial for enhancing the final products’ fuel efficiency, range, and safety standards. Furthermore, the electronics industry in Asia Pacific creates a significant demand for high-performance semiconductors. As per a study conducted by the Semiconductor Industry Association, ~75% of global semiconductor capacity is based in East Asia. Building manufacturing facilities in the region is likely to benefit semiconductor companies with up to 25–50% cost savings.
The unique properties of scandium make it an attractive material for the production of high-speed and energy-efficient electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and data centers. The electronics industry in Asia Pacific is experiencing exponential growth, driven by rising consumer demand for smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other electronic devices. Scandium-containing materials play a crucial role in electronic manufacturing, particularly in semiconductor production, where scandium oxide is used as a dopant to enhance the performance and reliability of semiconductor devices. Further, advancements in extraction and processing methods are expected to contribute to the scandium market progress in the region.

Surging Adoption of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Drives Scandium Market Growth
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), known for their high efficiency and low emissions, are gaining traction as a promising alternative to conventional power generation technologies in various sectors, including stationary power generation, transportation, and portable electronics. Scandium plays a pivotal role in SOFC technology, particularly in the form of scandium-stabilized zirconia (ScSZ). Used as an electrolyte in these cells, ScSZ improves ionic conductivity at elevated temperatures, enabling efficient ion transport across the cell and enhancing overall performance. This results in higher energy conversion efficiencies and enhanced durability, making SOFCs more attractive in an array of commercial and industrial applications. The surging demand for clean energy owing to environmental concerns and regulatory pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is fueling the adoption of SOFCs worldwide. Thus, the increasing adoption of SOFCs contributes to the growing scandium market size. Additionally, the surging popularity of electric vehicles is likely to bring new growth trends in the scandium market.
Scandium Market: Segmental Overview
The global scandium market is segmented on the basis of derivative and application. Based on derivative, the market is segmented into oxide, iodide, alloy, zirconia, and others. The iodide segment accounts for a significant share of the scandium market. Scandium iodide (ScI3) is classified as a rare earth halide and is characterized by its distinctive pink color in its solid form. Scandium iodide is primarily utilized in the field of materials science, particularly in the development of novel electronic and optical materials. Its optical properties make it valuable in the production of specialized lenses and filters for various optical instruments. The most important characteristic of scandium iodide is its potential application in solid-state lighting technology. Researchers are exploring the use of scandium iodide as a phosphor material to enhance the efficiency and color rendering of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Additionally, this compound has garnered attention in the nuclear energy sector due to its promising application in the manufacturing of radiation detection devices. Its high scintillation efficiency makes it suitable for use in detectors for gamma-ray spectroscopy and positron emission tomography (PET) imaging systems. Further, the magnetic properties of scandium iodide make it a subject of interest in the field of magnetism and magnetic materials. Researchers are investigating its potential as a component in magnetic refrigeration systems, which could offer a more efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional refrigeration technologies.
Based on application, the global scandium market is segmented into aerospace and defense, solid oxide fuel cells, electronics, ceramics, lighting, nuclear applications, 3D printing, and others. The solid oxide fuel cells and ceramics segment accounts for a significant market share. Scandium plays a crucial role in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), a promising technology for clean and efficient energy conversion. Scandium, typically yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), is primarily used as a dopant in the electrolyte material in SOFCs. When scandium is added to YSZ, it enhances the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte, facilitating the movement of oxygen ions between the cathode and anode at high temperatures. The incorporation of scandium into the YSZ electrolyte lattice helps mitigate grain boundary resistance, which is a significant factor limiting the efficiency and performance of SOFCs. By reducing the resistance to oxygen ion transport, scandium doping enables SOFCs to operate at lower temperatures, thereby improving their efficiency and reliability. The lowered operating temperature also extends the lifespan of SOFCs and reduces material degradation, contributing to their commercial viability. Currently, Bloom Energy is the only company that is using the scandium doping technology commercially and has also patented the design. This technology in the electrolyte material allows for thinner electrolyte layers in SOFCs, which leads to reduced ohmic losses and improved power density. This enhancement in power density is particularly beneficial for portable and decentralized energy applications, which require compact and lightweight fuel cell systems. Further, scandium oxide nanoparticles have shown potential as catalysts for the electrochemical reactions occurring at the cathode and anode interfaces in SOFCs. These nanoparticles can promote oxygen reduction and fuel oxidation reactions, further enhancing the performance and efficiency of SOFCs. Scandium oxide also serves as an essential dopant in ceramic formulations, allowing for the precise modification of material properties. By incorporating scandium oxide into ceramic matrices, manufacturers can tailor characteristics such as electrical conductivity, dielectric constant, and mechanical strength to meet specific application requirements. Owing to such versatility, scandium-doped ceramics are used in a wide range of applications in the aerospace and automotive industries, including high-performance electronic components, catalytic substrates, and structural materials. Scandium–aluminum silicates, formed by incorporating scandium into aluminum silicate matrices, exhibit enhanced thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance compared to conventional ceramics.
Scandium Market: Competitive Landscape
Scandium International Mining Corporation, American Elements Inc, NioCorp Development Ltd, Strategic Metal Investments Ltd, Rio Tinto, US Research Nanomaterials Inc, Otto Chemie Pvt Ltd, Stanford Advanced Materials, Heeger Materials Inc, and Hunan Oriental Scandium Co Ltd. are among the prominent players profiled in the scandium market report. In addition, several other players have been studied and analyzed during the study to get a holistic view of the market and its ecosystem. The report also includes company positioning and concentration to evaluate the performance of companies.